This blog is about how to run script on the server(s) using Ansible. You need to follow some various steps to run the script on hosts. It is very useful and helpful for a IT Admin to handle thousands of hosts using one command. You need to configure your hosts as well as your local machine from which you want to run the command.
Let’s Get Started
To run the script from your machine to host(s) you need to create a user for Ansible or change the configuration for existing user. To see this in detail you can refer this blog https://thejsdeveloper.wordpress.com/2020/08/06/getting-started-with-ansible/ Let’s see in breif what changes are needed to run script.
- You need to allow no password for user in host. To do that run:
$ sudo visudo
Add the line<user> ALL=(ALL:ALL) ALL - You need to have passwordless entry for the user in order to use Ansible, for that you need to follow these commands.
$ ssh-keygen$ ssh-copy-id -i ~/.ssh/id_rsa.pub <user>@<host>
Now try logging in to the host to check whether it needs a password or not, for that run:$ ssh <user>@<host>
This should log you in to the host without password. Otherwise Ansible will show the error of permission denied.
Running the script on Host machine
- Create a directory in which we will place all the files related to Ansible.
$ mkdir Ansible && cd Ansible - Create a shell script which you want to run. Note that the given script is of bash shell.
$ vim create-file.sh
Content for this file#!/bin/bash
touch /tmp/ansible_script_file - Create a configuration file for Ansible and paste the given content.
$ vim ansible.cfg[defaults]
inventory = ./inventory
retry_files_enabled = False
[ssh_connection]
pipelining = True - Create a file inside directory ./group_vars/ubuntu.yml. If you have more than one host you need to create different file for each host to specify some detail in it. The content inside the file will be:
---ansible_user: <username>
ansible_python_interpreter: /usr/bin/python3
ansible_usern => User for ansible on host machine
ansible_python_interpreter => You need to define the path of python interpreter if it is by default other than /usr/bin/python - Create file named ‘hosts’ inside the ./inventory directory. The content for the hosts file will be:
[ubuntu]
ubuntu_host ansible_host=<host>
In this file ubuntu_host is the host name like this there could be multiple host name in this file. - Now create the Playbook for Ansible. In this file all the instruction will be given to Ansible.
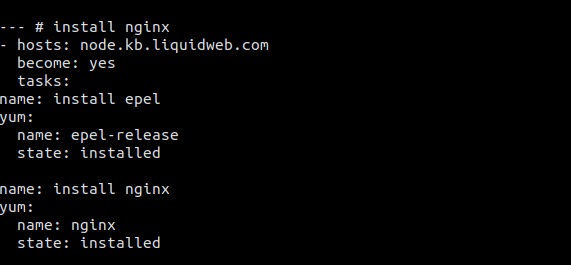
$ vim create-file-playbook.yml
Content for this file:---
- name: Transfer and execute a script
hosts: "*" # It will match all the hosts in you ./inventory/hosts file
tasks:
- name: Copy shell script
copy: src=/home/<local-machine-username>/ansible/file-create.sh dest=/opt/ansi mode=0777
- name: Executing shell script
command: sh /home/<username>/create-file.sh - Your directory structure is going to look something like this

- You are ready to rock. Now run the playbook command of Ansible to run the playbook.
$ ansible-playbook create-file-playbook.yml
You will see output like this…

That’s all for it. I hope this helped you to solve your problem. Have a nice day!