Use `console.log()` like a pro

Escape the vendor-locked in edge-runtime!
Sevalla is the home to your web projects. Host and manage your applications, databases, and static sites in a single, intuitive platform.
The most efficient AI coding agent
Use Cosine AI to automate your work in live codebases. It excels in large, existing codebases, where the real complexity (and business value) lives.
Using console.log() for JavaScript debugging is the most common practice among developers. But there is more.
The console object provides access to the browser’s debugging console. The specifics of how it works vary from browser to browser, but there is a de facto set of features that are typically provided.
I share a ton of JavaScript tips on Twitter, so be sure to check out my profile.
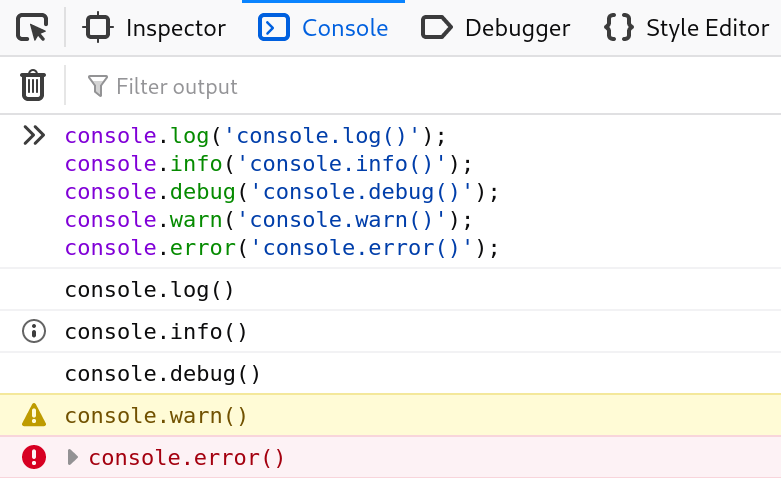
* The most common console methods:
console.log(): For general output of logging information.console.info(): Informative logging of information.console.debug(): Outputs a message to the console with the log leveldebug.console.warn(): Outputs a warning message.console.error(): Outputs an error message.
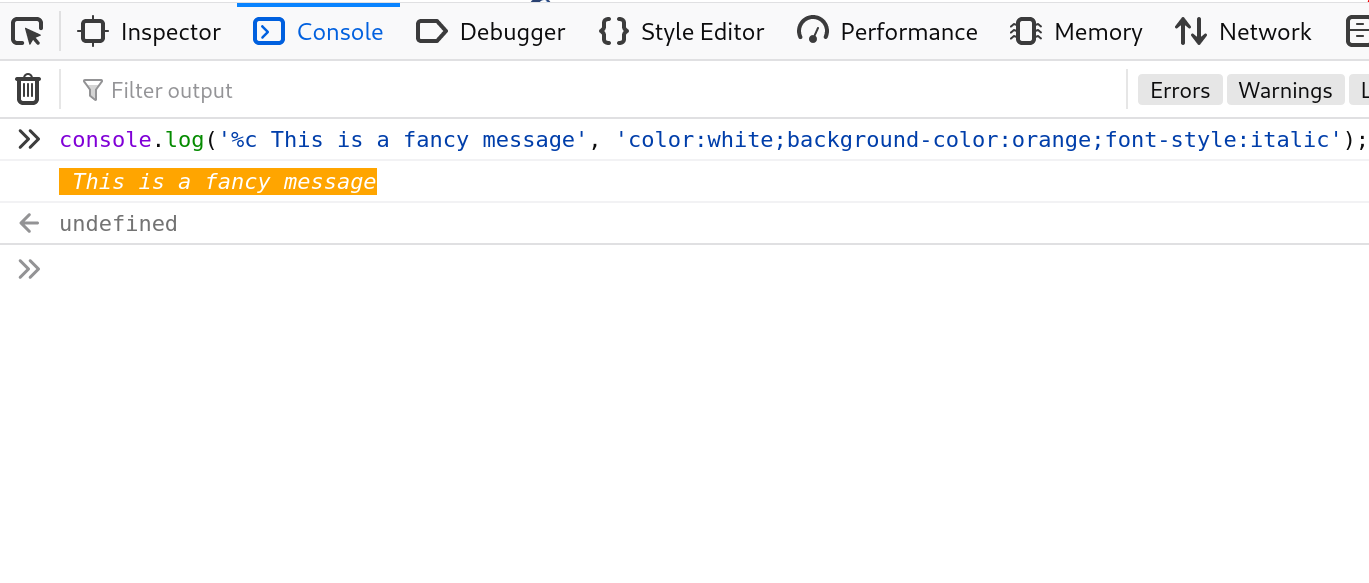
* Custom CSS styles for a console.log().
The console.log output can be styled in DevTools using the CSS format specifier.
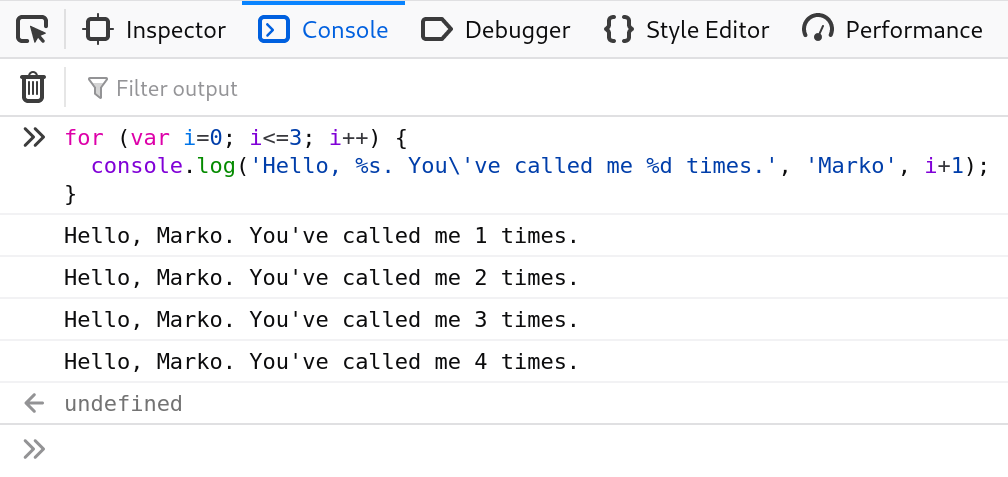
* String substitutions.
When passing a string to one of the console object’s methods that accepts a string (such as log()), you may use these substitution strings:
%s:string%ior%d:integer%oor%O:object%f:float
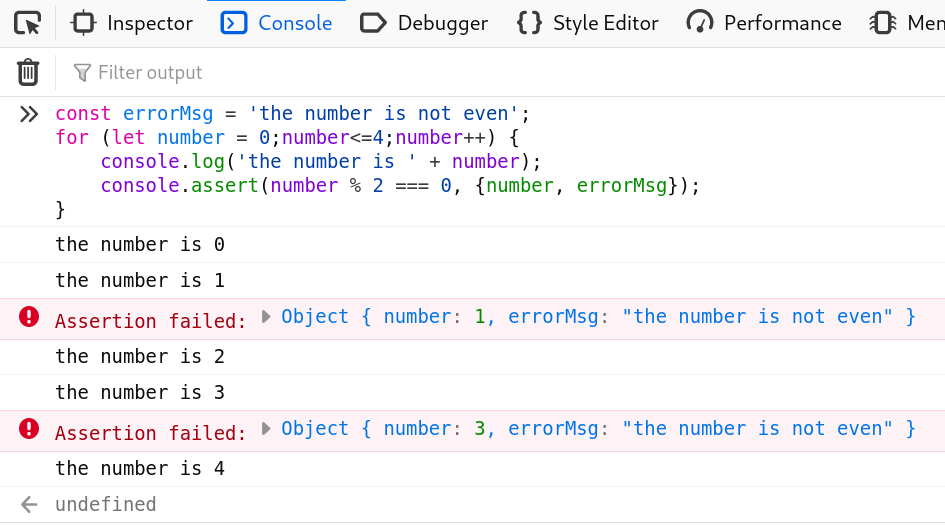
* console.assert().
Log a message and stack trace to the console if the first argument is false.
* console.clear().
Clear the console.
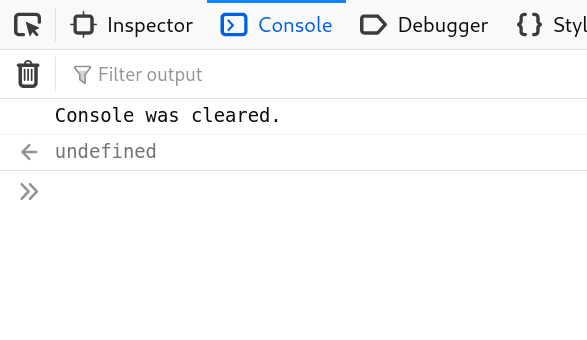
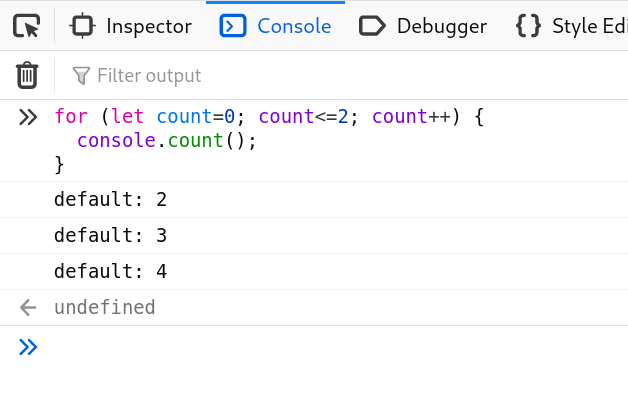
* console.count().
Log the number of times this line has been called with the given label.
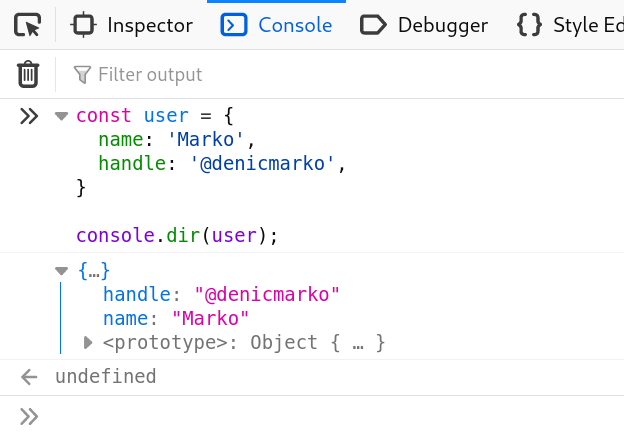
* console.dir().
Displays an interactive list of the properties of the specified JavaScript object.
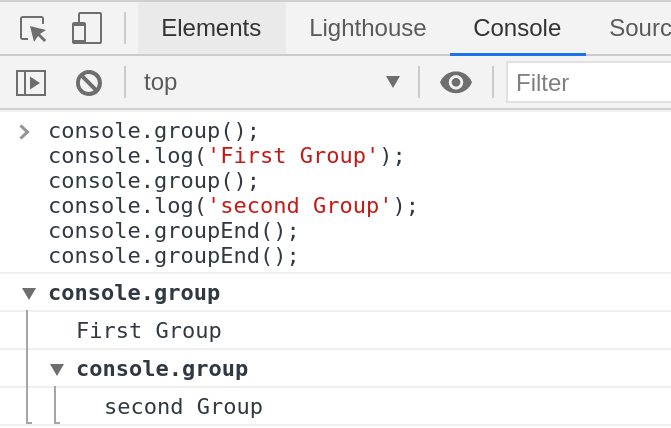
* console.group() and console.groupEnd().
Creates a new inline group, indenting all following output by another level. To move back out a level, call groupEnd().
* HTML elements in the console:
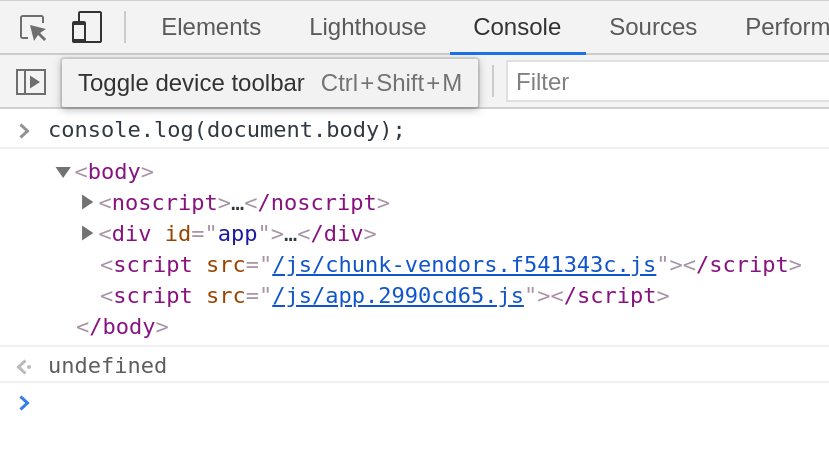
* console.memory.
The memory property can be used to check out the heap size status.
Note: memory is a property and not a method.
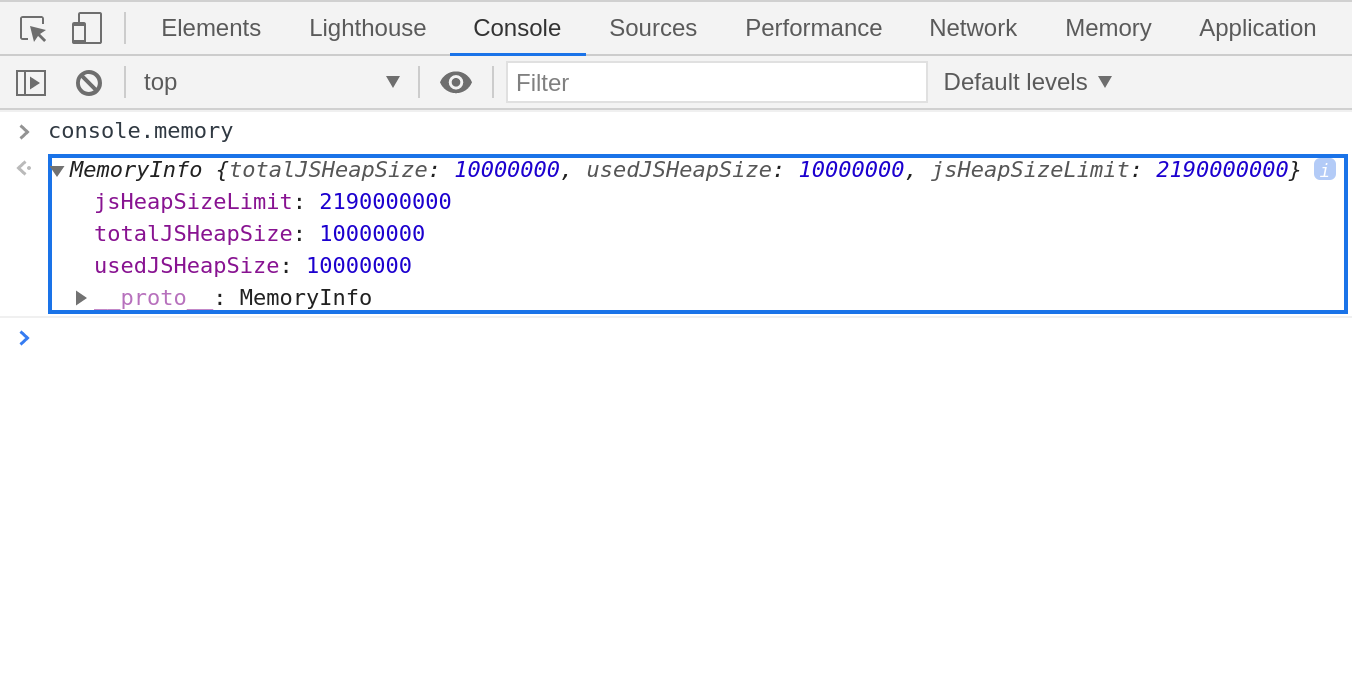
* console.table().
Displays tabular data as a table.
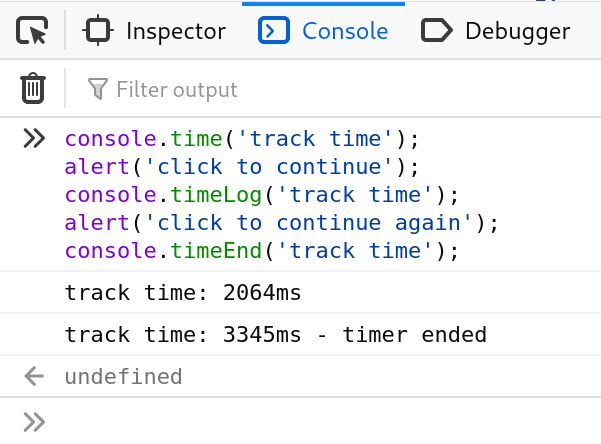
* console.time() and console.timeEnd().
console.time(): Starts a timer with a name specified as an input parameter. Up to 10,000 simultaneous timers can run on a given page.console.timeEnd(): Stops the specified timer and logs the elapsed time in seconds since it started.
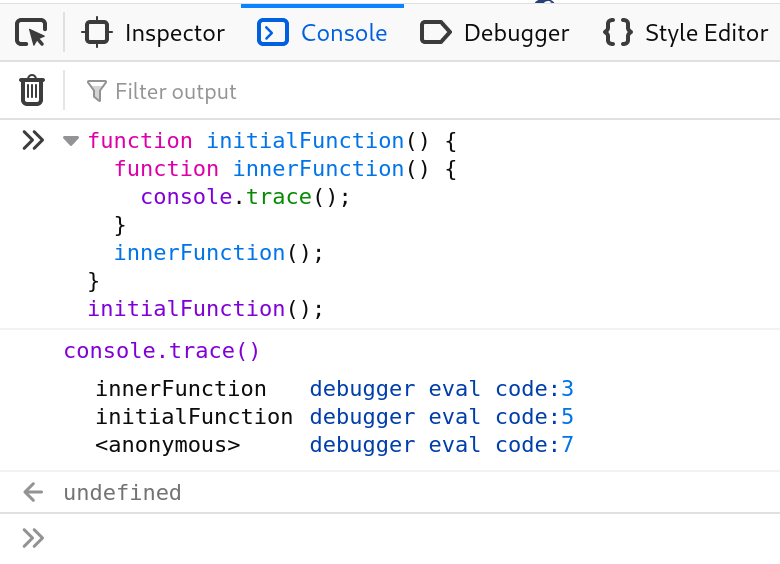
* console.trace().
Outputs a stack trace.
Which console method did you like the most? Let me know!