As Computer Science Students, we have to work on some Mathematical Problems while learning Java programming language. Calculating “Standard Deviation in Java” is one such Mathematical Problem.
Though Standard Deviation is a mathematical concept, when we work on Data Science or Software Development, finding Standard Deviation in Java will benefit us.
In this article, we will first briefly talk about the Standard Deviation. Later, we will show different processes to implement Java Standard Deviation. So, let us start our discussion.
Summary Or Key Highlights:
- Standard Deviation is a Mathematical Term by which we find out the Spread of Numbers in a Group.
- The Implementation Process of Standard Deviation in Java follows the Standard Deviation Formula.
- There are 3 Different Ways by which we can define Standard Deviation in Java Language.
- From Financial Analytics to Weather Forecasting, the use of Java Standard Deviation is everywhere.
- While working on Java Standard Deviation, we have to watch out for some Performance Implications.
What Is Standard Deviation? Read Below
Standard Deviation is a Mathematical Term that is used as a Statistical Metric. Using this statistical metric, we can find out the Amount of Variation or Dispersion in a dataset.
Standard deviation in Java is an essential concept used in statistical computations. You should consider us for help with your statistics assignments in Java especially when your project involves statistical functions like standard deviation.
In a Dataset, there can be 2 Types of Variations. Based on these variations, the Standard Deviation can be divided into two categories:
- Low Standard Deviation: When the Spread of numbers is close to the Mean.
- High Standard Deviation: When the Spread of numbers is not close to the Mean.
Let us make this understandable with the following example.
Set A: 80, 81, 79, 80, 82 [Average: 80.4]
Set B: 60, 90, 40, 100, 70 [Average: 72]
In these two datasets, the averages are nearly Similar (Approx. 80), but “Set A” has a Low Standard Deviation as all the values are close to the Average Value.
Whereas “Set B” will be the High Standard Deviation because some values are very far from the Average Value.
What Is The Formula Of Standard Deviation?
Now, we hope you have got some Basic Idea about the Standard Deviation from the above section. Now, let us move ahead to the discussion on the Standard Deviation Formula.
This formula will help to define Standard Deviation in Java easily. The formula is like the following:
Standard Deviation: sqrt( Σ (xi - μ)² / N )
The formula can be divided into the following sections or steps:
- At first, the Mean (µ) of the Dataset Values will be generated.
- Later, we have to subtract Each Value (xi) from the Mean (µ) and get the Square (xi − μ)².
- After that, all such Subtracted and Squared Values will be Summarized ( ∑ ).
- In the end, we have to divide that Summarized Value by the Number of Elements in the Dataset.
How To Calculate Standard Deviation In Java?
Now, after clearing the Formula of Standard Deviation in the above section, we can certainly move ahead to the Central Theme of the article. In this section, we will implement Standard Deviation in Java.
The Standard Deviation in Java can be calculated using 3 Different Methods. Let us start with the very first method, where we have to implement the entire formula and get the result.
1. Calculate Java Standard Deviation Using Loops:
In this method, we will implement the Standard Deviation Formula using Loops. Not only the Loops, but we will use different functions to make the code simpler and readable.
Here, the Standard Deviation Formula will be strictly followed, and the Formula Steps are implemented here in different functions. So, let us check the following code to know more.
public class Main
{
// Function To Calculate The Mean Or Average
public static double Mean(double[] zap)
{
double one = 0.0;
for (double z : zap) // For Loop To Add Values
one = one + z;
return one / zap.length; // Getting The Average
}
// Function To Calculate Standard Deviation
public static double StandardDeviation(double[] zap)
{
double m = Mean(zap); // Calling The Mean Function
double Sq = 0.0;
for (double z : zap) // Getting The Summation Of Squared Differences
Sq = Sq + Math.pow(z - m, 2);
return Math.sqrt(Sq / zap.length); // Calculating The Standard Deviation
}
public static void main(String[] args)
{
double[] zap = {12, 24, 33, 40, 85}; // Calling The StandardDeviation() Function
double one = StandardDeviation(zap);
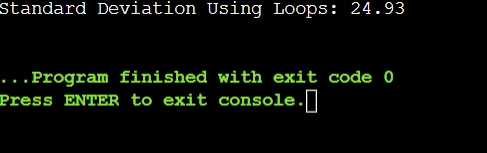
System.out.printf("Standard Deviation Using Loops: %.2f\n", one);
}
}
Steps Of The Program:
- At first, in the Main Function, the Dataset in the “Zap” Variable will be taken.
- Now, we will call the StandardDeviation() Function with the Dataset to do further work.
- In the StandardDeviation() Function, we will call the Mean() Function with the Dataset as the argument.
- In the Mean() Function, we will first add all the values and divide them by the Number of Elements.
- The Mean Result will come to the StandardDeviation() Function.
- With a For Loop, we will find out the Summation of Squared Differences using the “SQ” Variable.
- By dividing the “SQ” by the Number of Elements, we will return the Value to the Main Function.
Output:
2. Calculate Java Standard Deviation Using Streams:
Now, after Calculating Standard Deviation in Java using Loops and Functions, it is time to move ahead to some modern approaches where we have to invest less amount of work.
In this section, we will calculate the Standard Deviation using Java Streams. The Java Stream API only works on Java 8 or any Newer Versions. So, let us check the following code to know more.
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.List;
public class Main
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
List<Double> zap = Arrays.asList(12.0, 21.0, 35.0, 44.0, 59.0);
// We Will Calculate The Mean First
double m = zap.stream().mapToDouble(Double::doubleValue).average().orElse(0.0);
// We Will Calculate The Variance From The Mean
double v = zap.stream().mapToDouble(z -> Math.pow(z - m, 2)).average().orElse(0.0);
// We Are Getting The Standard Deviation
double one = Math.sqrt(v);
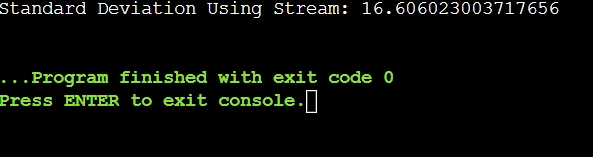
System.out.println("Standard Deviation Using Stream: " + one);
}
}
Steps Of The Program:
- At first, the Arrays and List Packages will be called into the program to work on them.
- Then, in the List Format, the Dataset Values will be taken, and it will be stored in the “Zap” Variable.
- Now, with the Stream() Function, we will use the MapToDouble() Method. From there, we will get the Average() Method, which will calculate the Mean in a single line.
- Now, using the same Stream() and MapToDouble() Methods, we will call the Average() to get the Variances. Here, the Summation of Squared Differences will be stored in the “V” Variable.
- In the end, we will do the SQRT using the MATH Package and get the output.
Output:
3. Calculate Java Standard Deviation Using External Library:
Last but not least method to calculate Standard Deviation in Java will be using some External Libraries like Apache Commons Math. Here, the workload of calculation is less than the other two methods.
In the Apache Commons Maths, there is the Descriptive Statistics Package, where the entire formula of Standard Deviation is mentioned. Let us check the following code to know its implementation process.
import org.apache.commons.math3.stat.descriptive.DescriptiveStatistics;
public class Main
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
DescriptiveStatistics zap = new DescriptiveStatistics();
double[] one = { 12, 40, 51, 30, 20, 15 };
for (double z : one)
{
zap.addValue(z);
}
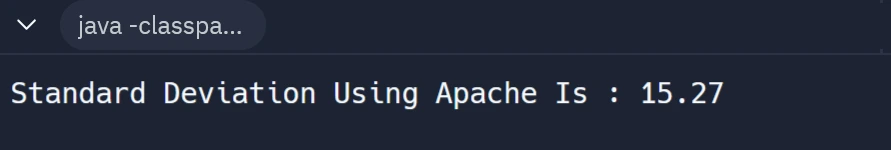
System.out.printf("Standard Deviation Using Apache Is : %.2f\n",zap.getStandardDeviation());
}
}
Steps Of The Program:
- At first, the Descriptive Statistics Package will be imported into the Java Program.
- Later, the “Zap” Object of Descriptive Statistics will be created that will be used in the next steps.
- Then, the “One” Variable will be declared where the Dataset Values are kept.
- Now, a For Loop will be executed where we will use the AddValue() Method with the “Zap” Object.
- In this For Loop, the Mean Value of the elements is generated by adding.
- In the end, we will use the GetStandardDeviation() Method to promptly get the result.
Output:
Comparison Table Between Java Standard Deviation Calculating Methods:
We hope that after such a detailed discussion, the Java Standard Deviation Calculating Methods have become clear to you. In this section, we will make them clearer using a Comparison Table.
In this section, we will make a Comparison Table on all Java Standard Deviation Calculating Methods based on some criteria like Readability, Performance, Flexibility, etc.
Criteria | Loop Method | Java Stream Method | External Library Method |
Approach | Manual | Functional | Library |
Code Complexity | High | Moderate | Low |
Readability | Moderate | High | High |
Performance | Moderate | Fast | Optimized |
Flexibility | Customizable | Limited | Extensive |
Learning Curve | Basic | Intermediate | Easy |
What Are Some Real-World Applications Of Calculating Standard Deviation In Java?
Calculating Standard Deviation in Java not only helps in Educational Purposes to develop strong problem-solving skills but also has many Real-world Applications that should be considered.
In this section, we will highlight some Real-world Applications for Calculating Standard Deviation in Java. This will help to encourage you to work and practice such problems more.
1. Financial Analytics:
When we are developing any Financial Applications with the Java Language, we will feel the need to calculate the Standard Deviation every time as it can be used for various purposes.
When To Use In Real-World Applications:
- In any Trading Application, we can calculate the Fluctuation of Stock Prices using Standard Deviations.
- In any Financial Portfolio and Investment Strategy, it helps to analyze the Risk Involvement.
2. Sports Analytics:
Not only in the Financial Sector but also in the Sports Industry, the use of Standard Deviation is high. In any Sports Application, calculating the Standard Deviation is needed to understand player performance.
When To Use In Real-World Applications:
- Across multiple matches or sessions, the Standard Deviation helps to assess Player Performance.
- Calculating Standard Deviation, we can find Stable or Fluctuating Players in any team.
3. Weather Forecasting:
Using Java Programming Language, if we are developing any Climate and Meteorological Applications, then calculating Standard Deviations will become important to analyze weather patterns.
When To Use In Real-World Applications:
- We can find out the Variability in Temperature or Rainfall Data over different periods.
- We can detect Unusual Weather Behaviors and forecast them to avoid calamities.
What Are Some Performance Implications Of Calculating Standard Deviation In Java?
We hope that whatever we have discussed till now will be enough to clear your understanding about the Standard Deviation Calculation in Java. However, while working on Java Standard Deviation, we have to keep in mind some Performance Implications.
In this section, we will let you know some Performance Implications that are necessary to remember.
- If we are Calculating Standard Deviation with a Large Dataset, the Memory Consumption will increase.
- While Calculating Standard Deviation, the Inefficient Loops can reduce the Performance.
- If the Traversal of the Dataset is performed frequently, then it will impact the Runtime Performance.
- If we use External Libraries like Apache, the Dependency Overhead will be introduced.
- If we are using Java Streams, then due to Parallel Streams, the Execution Speed will be hampered.
Conclusion:
In the end, we can say it is very important to know how to calculate “Standard Deviation in Java”.
However, we will advise you to clear the Basics of Java Programming before starting such a complicated Mathematical Problem. If your Java Basics are clear, you will find this concept a cakewalk.
Takeaways:
- Using Loops, Java Streams, and External Libraries, we can calculate the Standard Deviation in Java.
- If we use Loops, we have to follow the Formula in a Step-by-Step manner.
- The Java Streams reduce the workload to some folds to calculate the Java Standard Deviation.
- As the External Library, we can use the Apache Commons Math Package to calculate.
- We have to use the GetStandardDeviation() Method to promptly get the Standard Deviation in Apache.